Executive Summary
A coupon bond is a type of debt security that pays the holder periodic interest payments and repays the principal at maturity. The formula to calculate the present value of coupon bonds involves discounting the future cash flows (coupon payments and the face value of the bond at maturity) at a specified discount rate (r). It’s an essential tool for investors and financial analysts to determine the fair value of a bond and assess if the bond is priced appropriately in the market.
Formula Deep Dive
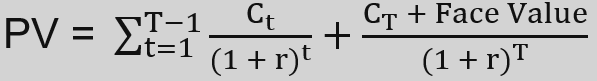
- Present Value (PV): represents today’s value of the zero-coupon bond
- Face Value: is the amount the bond will be worth at maturity (its par value)
- Discount rate (r): is the discount rate, reflecting the market interest rate or the required rate of return for the bond.
- Time to Maturity (T): represents the total number of years until the bond matures.
- Coupon Payments (Ct): are made by the bond at each period t until maturity. Typically, these payments are fixed and known in advance.
In practical use, the formula helps in understanding the relationship between the bond’s price, its coupon payments, maturity, and the market interest rate. It is widely used by investors to compare the return on bonds with different characteristics or against other investment opportunities.
Application in Excel
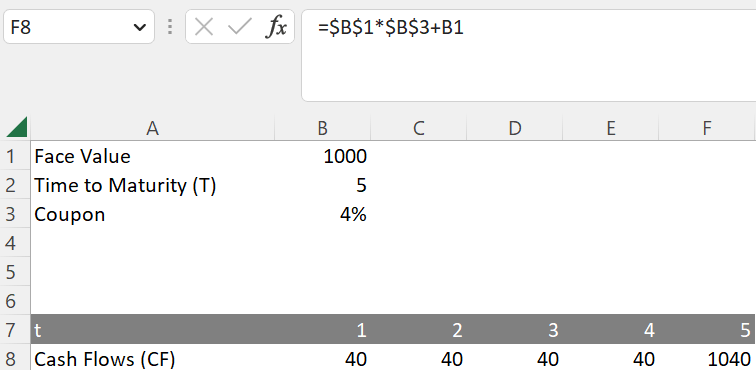
The PV of a coupon bond can be calculated in Excel in a few simple steps. The example below shows a coupon bond with a face value of 1000 (cell B1), a time to maturity of 5 years (cell B2) and a coupon of 4% (cell B3). One of the most practical ways to calculate the PV of the coupon bond is to use the SUMPRODUCT function. This can be facilitated by inserting the cash flows of the bond and the discount factors. In the example below, the cash flows of the bond can be calculated as follows:
=B1 * B3 (for year 1 to year 4)
=B1 * B3 + B1 (for year 5 to include the payment of the face value)
To apply the SUMPRODUCT function, the discount factors 1/(1+r)^t need to be calculated. The formula below provides the discount factor for year 5 and can is applied applied for all year respectively:
=1/(1+F10)^F7

The SUMPRODUCT function below calculates the bond price by multiplying the sums of cash flows and discount factors for each year t (CF1 * Discount Factor1 + CF2 * Discount Factor2 + … + CFT * Discount FactorT).
=SUMPRODUCT(B8:F8,B11:F11)
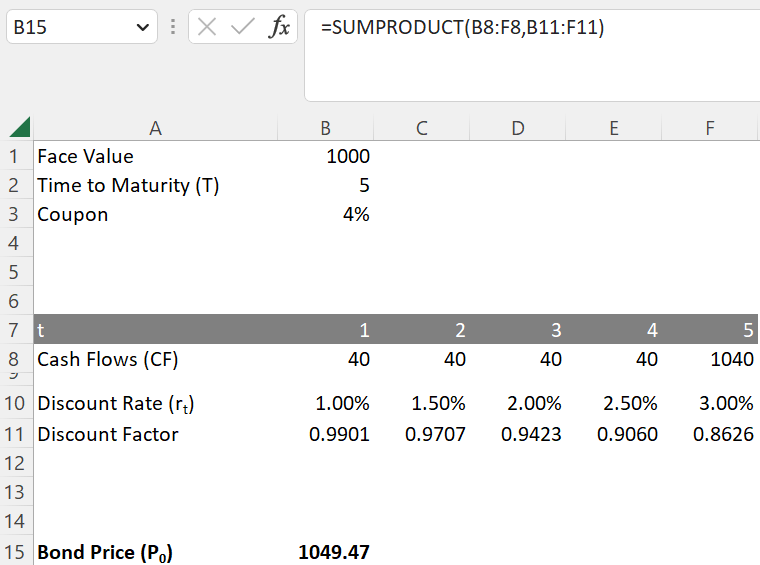
This Excel calculation breaks down the bond’s valuation into its constituent cash flows, allowing for a granular understanding of how each payment contributes to the overall value of the bond.
See also:
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is for educational purposes only and is not intended for use as legal, financial, or tax advice. While every effort is made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the content, Maths for Finance makes no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. In no event will Maths for Finance be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website. Please further review our Terms of Service.

